Creating an ideal environment for cannabis plants is only feasible if we understand the principles of nature - we cannot ignore the light spectrum.
Most cannabis growers have several goals in mind when planning an indoor crop. Achieve higher yields, increase THC level, or simply improve plant health. This strategic planning implies having knowledge in various scientific fields and linking the theory to technical solutions that contribute to achieving the proposed objectives. Apart from dedication and passion, what makes a good grower different from an expert is the desire to learn - so let us inform you of what it takes to grow cannabis of exceptional quality. Today we are going to discuss the fundamentals of physics, and understand how the light spectrum affects the growth of a cannabis plant.
What is light spectrum?
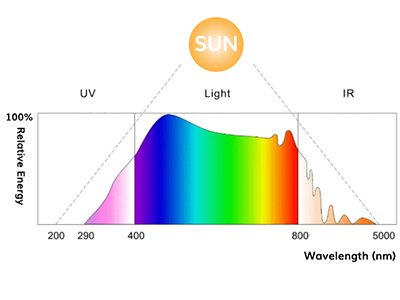
The sun emits energy in the form of solar radiation that includes gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, and even radio waves. Life on Earth is only possible because the ozone layer blocks this radiation. This filtration only allows wavelengths of between 300 and 1100nm to reach our plants, and only a portion of this light is visible. It is usually called light spectrum, color spectrum or visible spectrum, and ranges between 380nm and 750nm.
180-280nm - UVC: Extremely harmful, although luckily it is almost completely absorbed by the ozone layer
280-315nm - UVB: Causes skin burns and is believed to increase the level of THC.
315-400nm - UVA: It is not absorbed by the atmosphere, commonly known as black light.
380-750nm - Visible light spectrum: The bands of each wavelength represent the visible colors
700nm-1mm - Infrared light: Invisible above 750nm, but it shows as heat on the skin.
How the light spectrum affects plant growth
Every living organism needs information about what is happening around it in order to react to environmental changes and, in theory, gain a slight advantage over other members of its species. Cannabis plants receive much of this information in the light to which they are exposed and react almost immediately to the different bands of a wavelength - a very complex subject that would occupy several books, but let's focus on the basics.
1. Vegetative stage - "blue" light for healthy leaves (range: 400-500nm; ideal: 460nm).
During the vegetative stage, it is recommended to concentrate the light on the leaves as much as possible and ensure that the plants are compact, that they do not stretch too much, and that they develop strong stems. To achieve these goals, indoor growers often use metal halide lamps, fluorescent tubes or energy-saving light bulbs (CFL), and blue-band T5 / T8 lights during the first few weeks. When cannabis grows wild, the angle of the sun in spring lets more "blue" waves pass into the atmosphere, a signal for cannabis plants to develop large, strong and healthy leaves.
2. Flowering Period - "red" light for huge buds (range: 620-780nm; ideal: 660nm).
When cannabis plants begin their flowering period, higher yields can be obtained by exposing them to a light spectrum with lots of "red" waves, which stimulate the development of buds. The rate of photosynthesis reaches its peak when plants are subjected to "red" wavelengths of 660nm, although a NASA discovery indicates that "green" waves, which are not closely related to photosynthesis, also They can have an effect on how plants grow. Seeing a cannabis plant as a simple photosynthesis factory is therefore a bit rushed. But for now, the best way to mimic the angle of the sun in late summer / early fall is to choose a light with a high degree of "red" in its spectrum.
Increase THC level with UV lights - myth or reality
Have you ever wondered why the most potent varieties usually come from native plants in high altitude areas? Many experts believe that ultraviolet light, especially high exposure to ultraviolet wavelengths (280-315nm), is responsible for the increase in THC production. This theory is based on the higher elevation, the lower atmosphere between cannabis and the sun, which means greater exposure to UV rays. These ultraviolet rays damage our skin, and the human body reacts by producing melanin - the cannabis plant is supposed to do something similar - produces more resin and THC as a kind of sunscreen. It is too early to say if we are facing a more profitable theory or method to grow better cannabis, but the concept seems plausible enough to carry out our own experiments. UVB reptile lights are cheap; We should try.
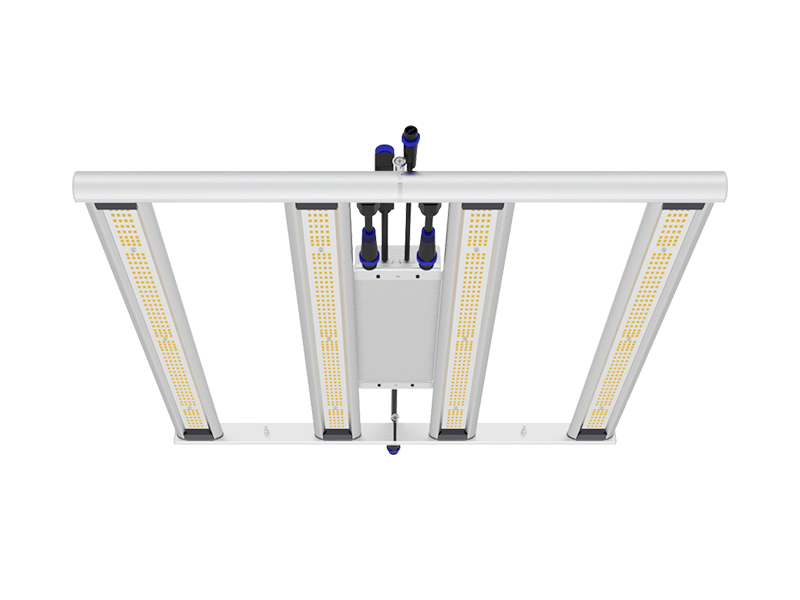
We have designed the newest 600W LED grow light with UV IR for cannabis cultivation, feel free to contact us to know more details about it.