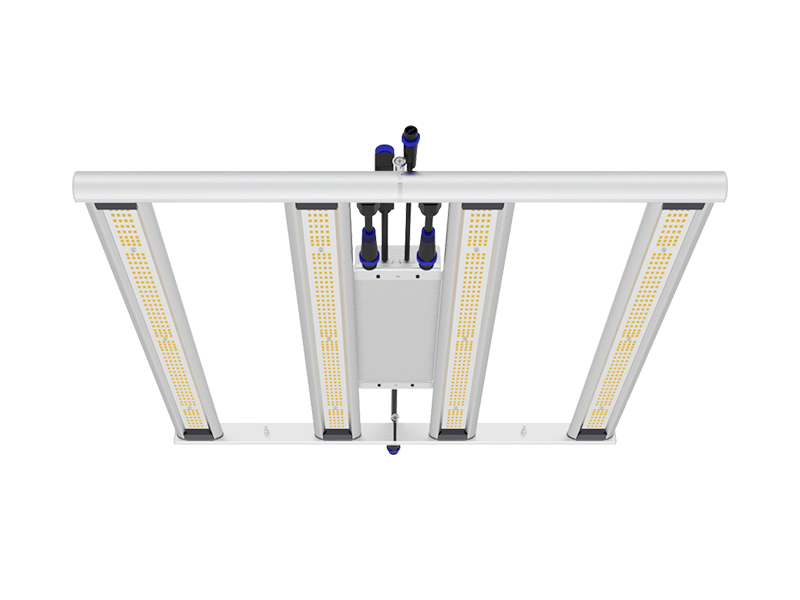
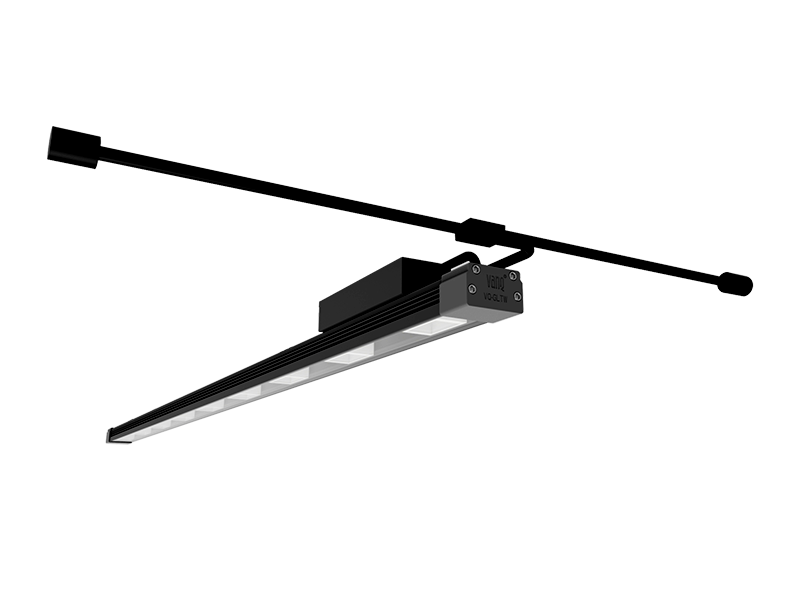
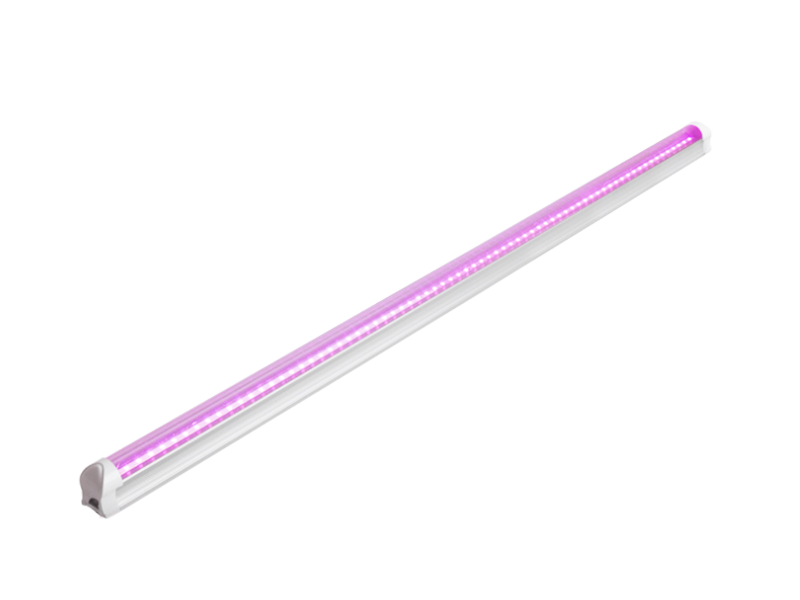
For a long time, sodium vapor lamps have been considered the gold standard for plant lighting-no other light source can achieve such high light output. However, in recent years, the development of LED technology has made a leap, and LED is about to surpass other light sources.
What is the use of plant lighting?
Together with water and carbon dioxide, light is one of the most important components of plant growth. With the help of green chlorophyll, plants convert sunlight into nutrients-a well-known process of photosynthesis. If the leaves cannot get enough high-quality light, growth will be blocked and the plant's vitality will be weakened.
Therefore, artificial light is sometimes used in plant cultivation. For example, if you want to prefer vegetables and herbs in winter, you must use professional plant lighting.
What kind of light do plants need?
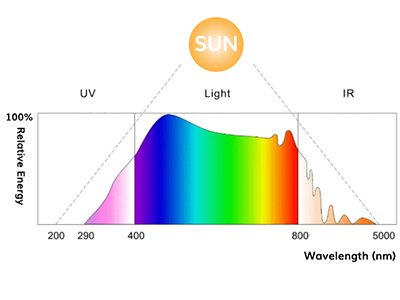
However, not all lights are the same. Because from a physical point of view, it is composed of electromagnetic waves. The length of these waves determines the color of light, and not every color can be used well for photosynthesis. The area available to plants is called PAR (photosynthetically active radiation), which lies between 380 and 780 nanometers. In addition, the green light in the middle area is less effective because most of it is reflected by the green leaves.
In order to measure the amount of light emitted by the lamp (which is useful for plants), the PPFD value is used: this value indicates how many photons of effective wavelength are emitted. When comparing plant lights, the PPFD value should always be used, as this only indicates how much growth-related light is emitted. Wattage or lumens has only limited meaning here.
Which lamps have been used for plant cultivation so far?
Until recently, many different light sources were used for the growth of indoor plants. However, the problem is that those lamps with high luminosity also have very high power consumption and a lot of heat. The following light sources were or very common:
Fluorescent tubes: They consume relatively little power, but do not produce great brightness. For many application areas of plant cultivation, lamps with higher light output are required.
Metal halide lamps: They are much brighter than fluorescent tubes and emit white light close to natural sunlight. However, the power consumption is high and the lamp becomes relatively hot.
Sodium vapor lamps: They have the best light output of all plant lamps, so they are very popular in situations where daylight must be completely replaced. However, they have some disadvantages: Sodium vapor lamps can become very hot and therefore require an additional powerful cooling system. They also consume a lot of electricity, and their light tends to move in the reddish spectral range, which is not ideal for the growth of most plants.
How does LED light work?

In order to make the LED (light emitting diode) emit light, the current must pass through the coated chip. The chip contains semiconductor crystals, which start to emit light when exposed to voltage. A single diode always emits light in a special color; the color of the light can be accurately determined by combining multiple diodes.
The origin of LED technology can be traced back 100 years, but some important developments have only recently appeared. In the past 20 years, the efficiency of light generation has been greatly improved. The range of light colors is also expanding: with special technology, even with neutral white light, LEDs can now provide a variety of colors.
What is the difference between LED lights and traditional lights?
For example, buying LED systems is still much more expensive than sodium vapor lamps. However, in some areas, the performance of LED lights is far superior to traditional grow lights:
The spectrum is fully adjustable: By mixing different LEDs, the color of the light can be precisely adjusted according to the needs of the factory. Therefore, light with high blue or red components can be generated, and ineffective green light can be omitted. LED is no longer lit according to the "watering can principle", but accurately generates the spectrum used by plants. Therefore, the LED system is characterized by a particularly high PPFD value.
Adapt to different growth periods: The optimal light color of many plants depends on the growth period in which they are located. LEDs can be used to meet these different needs. For example, many LED plant growth lights have a switch that can switch between the vegetation stage and the flowering stage.
Low heat generation: LED lamps hardly become hot during operation, which is a great advantage, especially when compared with metal halide or sodium vapor lamps. This can also save a lot of money and energy, otherwise, you will have to spend on cooling. It also has the advantage that the lamp can be placed closer to the plants.
Low power consumption: LED systems are also more economical than sodium vapor lamps in terms of power consumption: electricity costs can be reduced by up to 80%. This means that during a longer operating period, the operating cost of using LED lighting is lower than the operating cost of using other lights.
LED-the future plant lighting?
Recent developments have made LED technology an important alternative in the field of plant lights. In terms of light output, LEDs can now almost compete with traditional sodium vapor lamps, and they are much more energy efficient.
The power of the LED is particularly obvious under the color of the precise light distribution; there still seems to be some potential: by better adapting to the wavelength and higher PPFD value, the growth of certain plants may be significantly improved. It remains to be seen whether the current higher purchase prices will fall, and whether LEDs can completely replace other types of lighting in the future.