As a grower, you need to understand every growth stage of cannabis in cannabis cultivation. It is the basis of cultivation and the key to optimizing yield and quality.
Let us start with this topic in this article. Let us first study the life cycle of cannabis from a seed to an mature I will guide you step by step in to ensure that the growth environment is set up correctly and that the plant is properly taken care of. Are you ready? First of all, let us begin!
Budding Stage
When the humidity and temperature are suitable, the seeds break out of the shell, and the first white roots are revealed. Later, the seedling sprouted and pushed up the soil. At this time, young plants have the first pair of leaves, the cotyledons.
Environmental requirements
Temperature:Germination is ideal at 20-26°C. The seeds germinate too slowly below this temperature, and too much temperature will cause the seeds to die.
Humidity: High humidity is necessary, usually above 70%, which helps keep the soil moist and promotes root growth.
Light:Light is not required when the seeds are germinating. Once plants sprout from the soil, stable and dull light is necessary to aid in the onset of photosynthesis.
Germination process
Seed preparation:The seeds of most plants are soaked in warm water for 24 hours to soften the hard seed coat and speed up water absorption.
Sowing:The seeds are then carefully bedded on soft well-drained soil and covered with less dense soil to a depth of 0.5 to 1 cm and kept moist but not waterlogged all the time.
Root and Seedling Development:When the seed germinates, the roots are the first part to grow. They grow downward to help in supporting the plant and absorb water and nutrients. Afterwards, the seedlings’ stem grows upright, which displaces the cotyledons most effectively above the soil.
Stage duration
The germination stage usually lasts 1-2 weeks, depending on the type of seed and planting conditions.
Seedling Stage
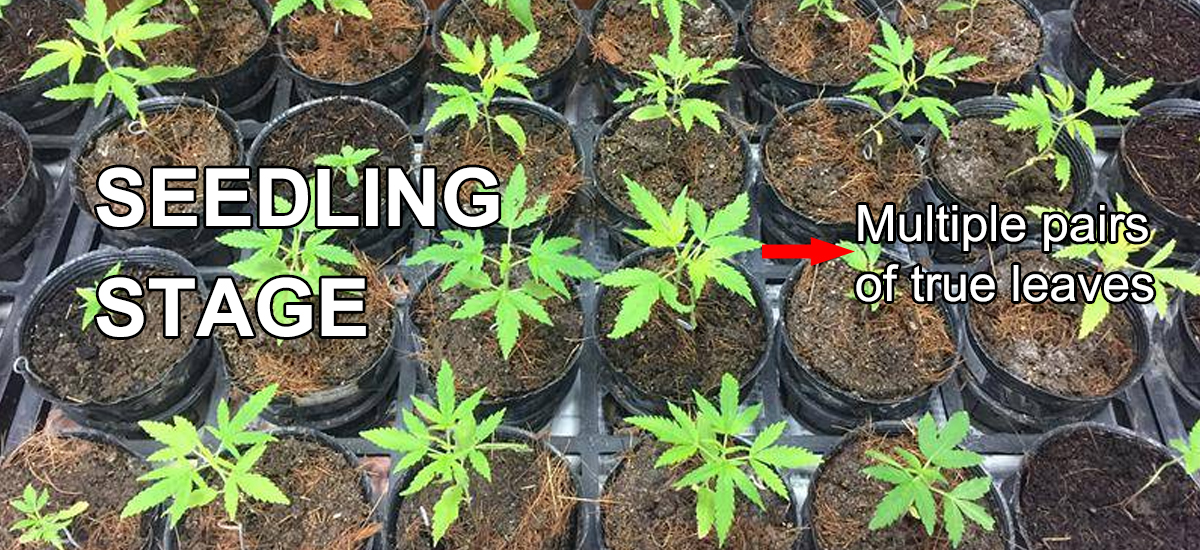

The tiny cotyledons plant develops into a multiple pair of true cannabis leaves. The true leaves have the typical cannabis leaf shape, as the number of leaves grows, the plant stems thicken.
Environmental requirements
Light:Seedlings need sufficient light to support their rapid growth. The best choice is a full-spectrum LED grow light with 16 to 18 hours of light every day.
Temperature:maintain 20-24°C in the ambient and night is no lower than 18°C.
Humidity:keep the relative humidity at 60% to 70%, too high humidity will cause mold to generate in the plants and too low will cause the young plants to wilt.
Ventilation: keep good air circulation.
Nursing measures
Watering:Roots develop in the ground should keep moist, and using a sprayer spray of water is necessary. Do not use too much water to prevent root hypoxia and disease from occurring.
Fertilization:Use low-concentration fertilizers to avoid excessive nitrogen, which can harm seedlings.
Disease and pest management: Check plants regularly to detect any signs of disease or pest infestation. Use natural and environmentally friendly pest control methods, such as food-grade insecticides.
Stage duration
The seedling stage usually lasts 2-3 weeks, but this time may vary depending on environmental conditions and plant species.
Growth Period
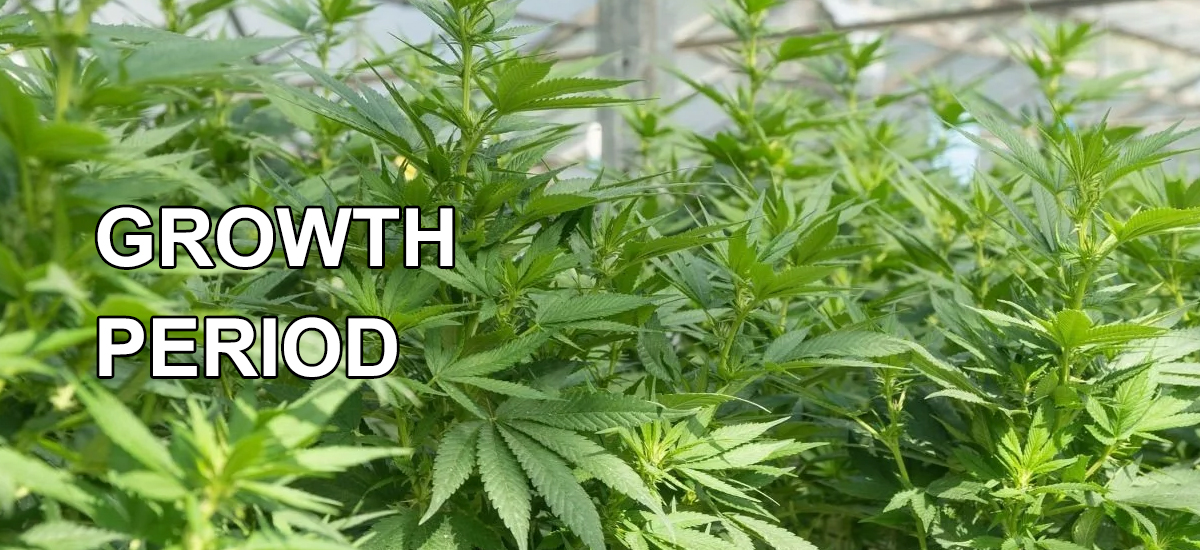

Cannabis plants will significantly increase their height during the growing season, growing several inches per week. The number and size of leaves increases, branches become thicker, and the overall plant shape becomes fuller and expanded. The plant's root system is also rapidly expanding to support the rapid growth above.
Environmental requirements
Light: Light is required for season growth, and full-function LED is ideal for providing 18-24 hours of daylight every day
Temperature: the temperature from day to night is 22-28°C, and the night should no less than 20°C this optimal range can maintain photosynthesis, regulate growth rates, etc.
Humidity: keep perfect relative humidity between 40-60%, reducing it to prevent fungi and mold growth.
Ventilation: Ensure good air circulation, which not only reduces the risk of disease, but also promotes plants to absorb carbon dioxide more evenly, which is beneficial to their growth.
Nursing measures
Fertilization: Fertilization at this stage should be rich in nitrogen, as nitrogen is a key element that promotes leaf and stem growth. Apply a balanced NPK (nitrogen phosphorus potassium) fertilizer regularly, adjusting the fertilizer ratio according to the plant's growth response.
Pruning: Timely pruning can promote healthier growth and better light coverage of plants. Removing lower branches and leaves can focus energy on the top growing points.
Ventilation:Keep airflow, preventing disease
Stage duration
The growing season usually lasts 3-8 weeks, depending on variety characteristics and growing environment.
Flowering Period

Flowering is the most critical stage in plants’ growth. The buds gradually develop and open, revealing a thick flower covered in resin, which is the key source of cannabinoids. female cannabis flowers are covered white-haired filaments, which are the main source of thc and other cannabinoids.
Environmental requirements
Light: Adjust the photoperiod to 12 hours of light/12 hours of darkness during the flowering period, mimicking the lower light level in fall, which encourages plants to grow flowers.
Temperature: The temperature is maintained at 20°C to 26°C during the day and not lower than 18°C at night. Temperatures that are too high or too low may affect flower development and THC content.
Humidity: Control the humidity between 40% and 50%. Lower humidity helps reduce the risk of mold and promotes dense growth of flowers.
Ventilation: Good air circulation is essential to prevent disease and promote proper flower ripening.
Stage duration
The flowering period usually lasts 6-8 weeks and may vary between varieties of cannabis plants.
Maturity and Harvest
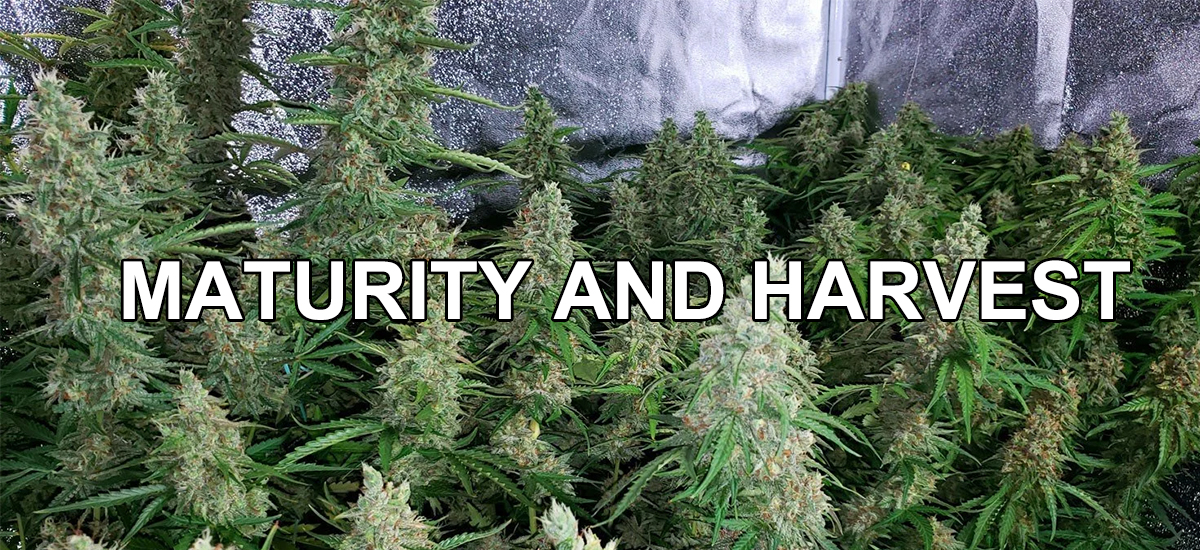

When the cannabis flowers are full and resinous, it is close to harvest time. Watching the plant's hair change from white to dark is an important indicator of maturity. During this stage, the cannabis flowers reach their optimal state of maturity and are ready for harvest.
Preparation before harvest
Flower Observation: Observe the hairs and resin glands of the flowers. It usually means the flower is mature when most of the hairs change from white to dark and the resin glands change from clear to cloudy or amber.
Nutrient flushing: 1 to 2 weeks before harvest, start flushing and replace fertilizer with clean water to remove residual nutrients and salts in the plants and improve cleanliness and taste when burning.
Harvesting method
Hand Harvesting: Harvest flowers by hand using scissors or professional pruning tools, which helps maintain the integrity and quality of the flowers.
Mechanical harvesting: Mechanical harvesting can be considered when planting on a large scale. Although it is fast, it may affect the integrity of the flowers.
Post-harvest handling
Drying: Hang and dry the harvested fruits in a well-ventilated, dark place, usually for 7 to 14 days, until the stems can break easily.
Curing: The dried flowers should be placed in a sealed container for curing, and the lid should be opened and ventilated regularly to remove remaining moisture and gas. This process helps enhance the flavor and potency of the flowers.
To grow good cannabis, understanding every stage of its growth from seed to harvest is key! This is the equivalent of creating a personalized growth plan for your plants, getting it just right every step of the way. When you meet the needs of each stage, your cannabis yield and quality will naturally increase.
If you have more questions about growing cannabis, or would like to learn more about grow lights and technology, you can contact us by clicking on the box below.